NEUROPHYSIOLOGY
NEUROPHYSIOLOGY
As the leading neurologist In PCMC, Dr. Sandeep Borse delves into neurophysiology, exploring the intricate functions of the nervous system. From examining entire organs to dissecting cellular networks, his expertise sheds light on generating and transmitting electrical impulses within neurons. This knowledge enriches our understanding of human cognition and enhances the diagnosis and treatment of neurological disorders.
EEG
An electroencephalogram (EEG) is a diagnostic test that records the electrical activity in the brain. It involves placing small metal discs called electrodes on the scalp to detect brain signals. These signals, representing the communication between brain cells through electrical impulses, are constantly present, even during sleep, and are depicted as wavy lines on the EEG recording
An EEG is one of the main diagnostic tests for epilepsy. An EEG can also play a role in diagnosing other brain disorders.

EMG NCV
Electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction velocity (NCV) are electrodiagnostic tests that measure the electrical activity of muscles and nerves. These tests may be an important part of a spine patient’s work-up by their doctor.
Visual Evoked Potential (VEP)
A visual evoked potential is an evoked potential caused by a visual stimulus, such as an alternating checkerboard pattern on a computer screen. Responses are recorded from electrodes that are placed on the back of your head and are observed as a reading on an electroencephalogram (EEG). These responses usually originate from the occipital cortex, the area of the brain involved in receiving and interpreting visual signals.

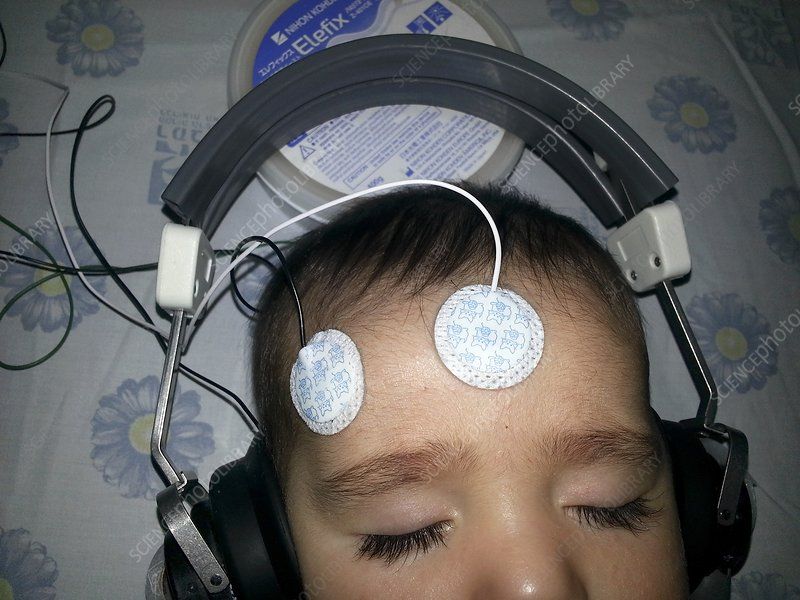
Brainstem Evoked Response Audiometry (BERA)
Brain Evoked Response Auditory (BERA) is a hearing examination performed on children aged 1 to 3 years. Meanwhile, for children with a smaller age, Oto Acoustic Emission (OAE) examination can be carried out. If the BERA test results are stated in good condition, it can be concluded that the child’s hearing function is within normal limits and no further medical treatment is necessary. However, if the BERA test results are declared abnormal, then the examination will continue with the estimation or prediction of the hearing threshold and hearing rehabilitation must be carried out as early as possible by using hearing aids. BERA test itself will take approximately one hour.
Somatosensory Evoked Potential(SSEP)
SSEP (Somatosensory Evoked Potential) is one of the many intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring tests that is used during a surgery. The SSEP test monitors the nerve pathways that are responsible for feeling pressure, touch, temperature and pain.